In a study of patients with episodic and chronic migraine who experienced 2-4 prior preventive category failures,1
Emgality delivered significant reductions in MHDs1
CONQUER: -4.1 days on Emgality 120 mg (n=232) vs -1.0 day on placebo (n=230) over Months 1 to 3 (baseline: 13.4 vs 13.0) (p<0.0001)1a
aLS means are present.
SELECT IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Contraindications
Emgality is contraindicated in patients with serious hypersensitivity to galcanezumab-gnlm or to any of the excipients.
EMGALITY SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCED THE BURDEN OF MIGRAINE IN BETWEEN ATTACKS2
Patients taking Emgality reported improvement in the burden of migraine in between attacks, as assessed by the MIBS-4.2
Mean change from baseline on the MIBS-4 was greater for patients treated with Emgality vs placebo.
Mean Reduction From Baseline in MIBS-4 at Month 32a
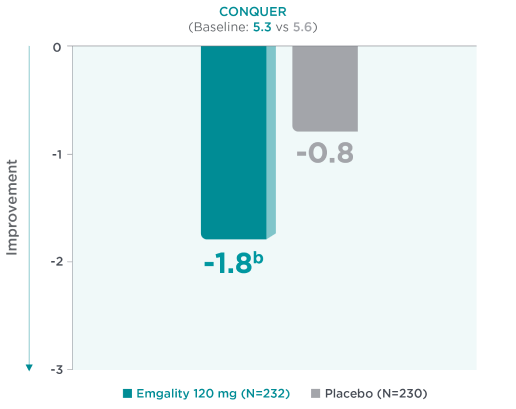
aLS means are presented.2
bNominal p-value ≤0.001 vs placebo.2
Mean reduction from baseline in MIBS-4 scores at Month 3a in CONQUER for Emgality 120 mg (N=232) was -1.8b vs -0.8 with placebo (N=230) (baseline: 5.3 for Emgality vs 5.6 for placebo, respectively).2
Statistical significance does not imply clinically meaningful difference.
Change in MIBS-4 from baseline to Month 3 was evaluated using an ANCOVA model controlling for prespecified effects. For missing MIBS-4 score at Month 3 (9 in placebo, 8 in Emgality 120 mg) LOCF was used. There was no adjustment for multiplicity in the treatment comparisons using the MIBS-4.2
MIBS-4 measures the burden of migraine between attacks, including disruption at work and school, diminished family and social life, difficulty planning, and emotional difficulty.3-5
- MIBS-4 is scored on a scale from 0 to 12. A score of 0 indicates no burden, 1-2 indicates mild burden, 3-4 indicates moderate burden, and scores ≥5 indicate severe burden
ANCOVA=analysis of covariance; LOCF=last observation carried forward; MHD=migraine headache day; MIBS-4=Migraine Interictal Burden Scale-4.
SELECT IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including dyspnea, urticaria, and rash, have occurred with Emgality in clinical studies and the postmarketing setting. Cases of anaphylaxis and angioedema have also been reported in the postmarketing setting. If a serious or severe hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue administration of Emgality and initiate appropriate therapy. Hypersensitivity reactions can occur days after administration and may be prolonged.
References
- Mulleners WM, Kim BK, Láinez MJA, et al. Safety and efficacy of galcanezumab in patients for whom previous migraine preventive medication from two to four categories had failed (CONQUER): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3b trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(10):814-825.
- García-Azorin D, Ford J, Buse DC, et al. Changes in work productivity and interictal burden: results from randomized, double-blind study evaluating galcanezumab in adults with treatment resistant migraine (CONQUER). Presented at: 17th Asian Oceanian Congress of Neurology (AOCN 2021); Taipei, Taiwan; April 1-4, 2021.
- Buse DC, Rupnow MF, Lipton RB. Assessing and managing all aspects of migraine: migraine attacks, migraine-related functional impairment, common comorbidities, and quality of life. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84(5):422-435.
- Buse DC, Bigal M, Rupnow M, et al. Development and validation of the Migraine Interictal Burden Scale (MIBS): a self-administered instrument for measuring the burden of migraine between attacks [abstract S05.003]. Neurology. 2007;68(suppl 1):A89.
- Buse DC, Bigal M, Rupnow M, et al. The migraine interictal burden scale (MIBS): results of a population-based validation study. Headache. 2007;47(5):778.